In this article, we are going to learn what is the specific gravity of cement, the specific gravity test of cement, and precautions to be taken while doing the specific gravity test of cement.
Table of Contents
What is specific gravity of cement?
The specific gravity of cement is defined as the ratio of the weight of a given volume of cement to the weight of water of the same volume.
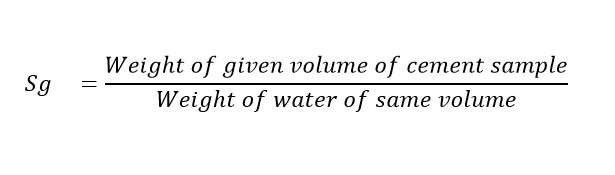
The specific gravity of any material gives us an idea about the behavior of that material in water. It is a number that denotes how many times a substance is heavier than water.
The materials which have a specific gravity less than the specific gravity of water is float on water and the material which have a specific gravity greater than the specific gravity of water is sinks in water.
As we know Specific gravity of water is 1. So, the materials with a specific gravity less than 1 are float on water while the materials with a specific gravity greater than 1 are sink in water.
The specific gravity of different construction materials are given below in table-
| Material | Specific Gravity |
| Water | 1 |
| Cast Iron | 7.20 |
| Steel | 7.82 |
| Sand | 2.55 |
| Aluminum | 2.72 |
| Gravel | 2.71 |
Specific gravity of cement range-
The specific gravity of cement ranges from 3.1 to 3.16.
This means the specific gravity of cement range is more than 1 thus cement sinks in water.
Importance Of Specific Gravity Test Of Cement-
Generally, cement used in construction has a specific gravity of 3.15. With the increase in moisture content in cement specific gravity of cement is also changed.
If the specific gravity of cement is more than 3.19 then it shows the cement is not perfectly minced into powder during its production or it has more moisture content. Which will affect the mix design and consequently the quality of construction.
A good quality cement has specific gravity ranges from 3.1 – 3.16. So it is important to test the specific gravity of cement before its use in construction to check its value is within the limit or not.
Specific Gravity Test of Cement-
We are going to do a specific gravity test of cement using le chatelier’s principle as per (IS 4031 (Part 11) 1988)
Apparatus-
Le Chatelier’s Flask
Kerosene
Cement
Weighing Balance with 0.1g accuracy
Why We use Kerosene instead of water in Specific Gravity Test Of Cement-
Generally, we use water as reference material in a specific gravity test of any material but in a specific gravity test of cement, we use kerosene as reference material because when we add water to cement, cement reacts with water and starts the hydration process.
When we add kerosene to cement it does not show any reaction with it. That’s why we use kerosene instead of water in a specific gravity test of cement.
The Specific Gravity of kerosene is 0.79
Procedure For Specific Gravity Test Of Cement-
1) Clean le chatlier’s flask properly it should be free from moisture.
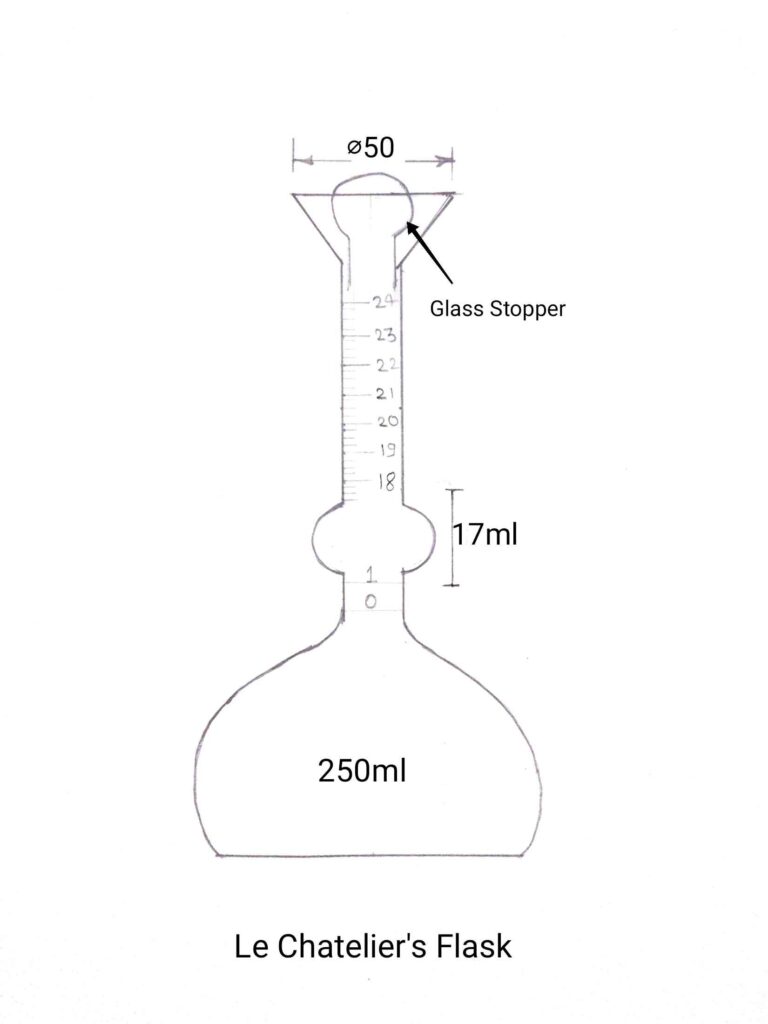
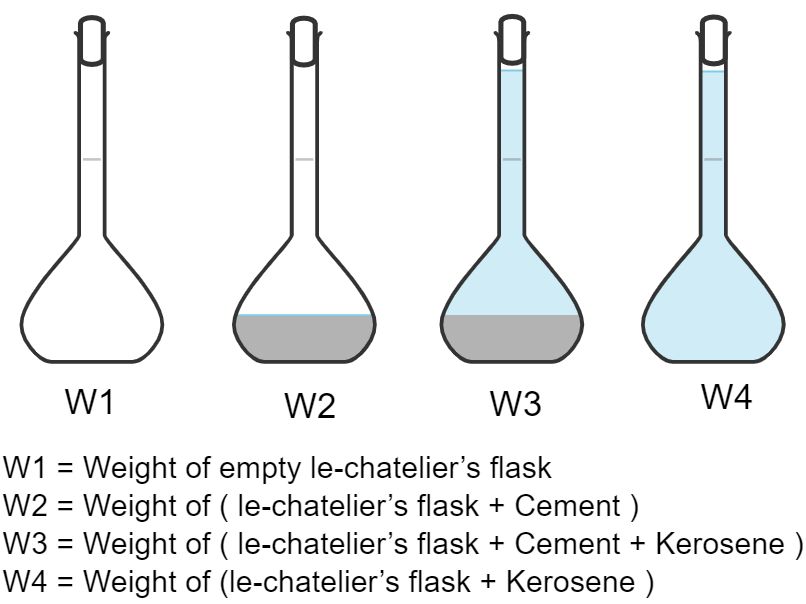
2) Take a weight of empty le chatlier’s flask and note it down as W1 (For better understanding refer to the image given below).
3) Now take 50g of cement and pour it in le chatlier’s flask and fixed the stopper on flask And take a weight of it and note down as W2
4) Now open the stopper of the flask and fill the flask up to its neck with kerosene.
5) Now fix the stopper again and shake the flask and see no air bubble left in the flask. Note down this weight as W3.
6) Now empty le-chatelier’s flask completely and fill the kerosene in the flask up to the neck. Note down this weight as W4.
7) Repeat the above procedure at least three times to eliminate the errors.
Observation Table-
| Description | Trial 1 | Trial 2 | Trial 3 |
| Weight of empty bottle (W1) | |||
| Weight of bottle + Cement (W2) | |||
| Weight of bottle + Cement + Kerosene (W3) | |||
| Weight of bottle + Full kerosene (W4) |
Now put these values in the specific gravity of cement formula given below-
Specific Gravity Of Cement Formula-
Specific gravity of cement = Weight of given volume of cement sample / Weight of kerosene of the same volume
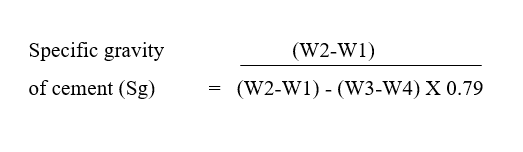
Where,
W1 = Weight of empty le-chatelier’s flask
W2 = Weight of ( le-chatelier’s flask + Cement )
W3 = Weight of ( le-chatelier’s flask + Cement + Kerosene )
W4 = Weight of (le-chatelier’s flask + Kerosene )
0.79 = Specific gravity of kerosene.
Repeat this process again three times and take an average of them for accuracy purposes.
Result –
The specific gravity of cement is = ……..
Precautions –
Kerosene used for specific gravity test of cement should be free from water.
Air bubbles should be removed while filling the apparatus.
Weighing should be done accurately and quickly after filling the apparatus and should be accurate to 0.1 mg.
At the time of weighing temperature of the apparatus should not be allowed to exceed the specified temperature.
FAQs On Specific Gravity Test of Cement –
What is the standard specific gravity of cement?
The standard specific gravity of cement is 3.15.
Specific Gravity Of OPC Cement?
The specific gravity of OPC cement ranges from 3.1 to 3.16.
Specific Gravity of PPC cement?
The specific gravity of PPC cement ranges from 3.06 to 3.08.
Specific gravity of cement IS Code?
IS 4031 (Part 11) 1988 is IS code for specific gravity of cement.
What is specific gravity of kerosene?
The specific gravity of cement is 0.79.
Also Read: Fineness Test of Cement
